Five Key Charts to Watch in Global Commodity Markets
Commodity I December 18, 2023
Summary
In agriculture, orange juice futures are set to take the crown as the top-performer among soft commodities changing hands in the Americas and Europe. Meanwhile, in oil markets, options are suggesting that a recent selloff may be overdone.
Here are five notable charts — well, actually, it’s four charts and one map — to consider in global commodity markets as the week gets underway.
Natural Gas
A natural gas trade known as the widowmaker due to its volatility is in focus as unseasonably warm weather in the US reduces demand for the heating and power plant fuel. The spread between March and April futures — essentially a bet on how tight supplies will be at the end of the North American winter — flipped to negative last week. That was the earliest dip below zero in the season on a closing basis since December 2020.
Oil
Brent futures are heading for their third straight monthly decline, but options traders are suggesting the selloff may have gone too far, with consumers seen hedging against a rebound. The call skew — which measures how much more buyers will pay for protection against declines in crude versus rallies — has started to recover after tumbling last month. Oil markets have shrugged off recent pledges by the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries and its allies to deepen supply cuts, instead sending futures to near a five-month low.
Agriculture
Orange juice has been crushing it this year. Futures for what was once a staple of many American breakfasts have soared by more than 80% — on track for their largest annual gain since 2009, according to ICE Futures US. The spike has come with production decimated by disease, extreme weather and a reduction of farmers in key growing areas.
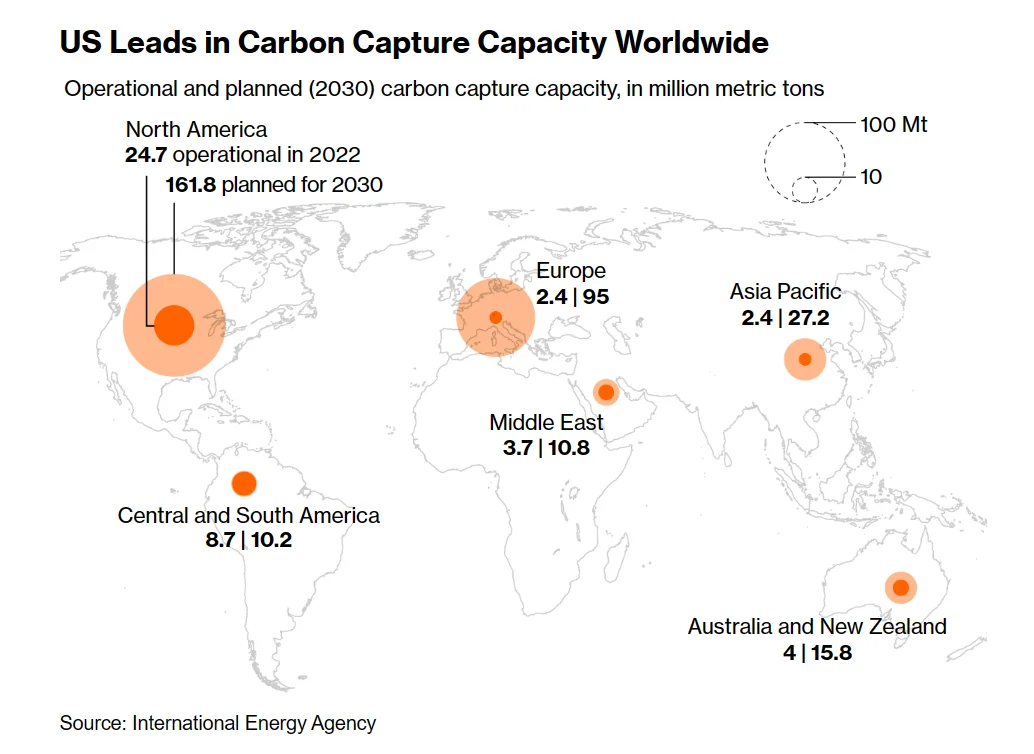
Carbon Capture

The world just inked a historic pact at the COP28 climate talks to move away from using fossil fuels. But it also endorsed a vital technology that could give them a lifeline: carbon capture and storage. The US is set to be the most important proving ground for the nascent technology to keep greenhouse gases from the atmosphere. The sprawling infrastructure required will include enough pipelines to circle the Earth four times.
Coal
Peak coal is here. Total consumption of the dirtiest fossil fuel will reach a record high of more than 8.5 billion metric tons this year, and then start a long, slow decline, according to the International Energy Agency’s Coal 2023 report released Friday. That shift lower will be driven by global efforts to boost clean energy and rein in carbon emissions.

Coal remains the world’s biggest source of electricity, but surging installations of renewables are outpacing rising demand for power.
Get PRO
Get access to exclusive premium features and benefits. Subscribe PRO plan.

